The Nipah virus (NIV) outbreak in West Bengal, India, continues to raise concerns worldwide. The virus, known for its high mortality rate, has affected at least five individuals, including three frontline healthcare workers. One of the patients is in critical condition. Nearly 100 individuals who came into close contact with infected patients have been placed under quarantine.
Current Situation
-Confirmed Cases: Five individuals have tested positive for the Nipah virus, including three healthcare workers. One patient’s condition is critical.
-Quarantine: Nearly 100 close contacts have been quarantined to prevent the virus from spreading.
-Healthcare Disruptions: Some healthcare facilities in the region have temporarily suspended non-emergency services due to the outbreak.
-Possible Source: The source of the outbreak has not been confirmed, but there is strong suspicion that it is linked to local fruit bats or consumption of contaminated date palm sap, a traditional food in the region.
-Border Measures: Thailand and Nepal have increased border screenings to prevent the virus from spreading across borders.
What is Nipah Virus?
Nipah virus is an emerging pathogen that poses significant health risks, with a mortality rate ranging from 40% to 75%. The virus is zoonotic, meaning it can be transmitted from animals to humans, and it can also spread through human-to-human contact. There is currently no vaccine or specific treatment available, which makes it an extremely dangerous threat.
The incubation period for Nipah virus typically ranges from 4 to 14 days but can extend up to 45 days. This extended latent period means that infected individuals can spread the virus for several weeks without showing symptoms, which makes controlling the outbreak even more challenging.
Transmission Routes
The virus can spread through multiple routes:
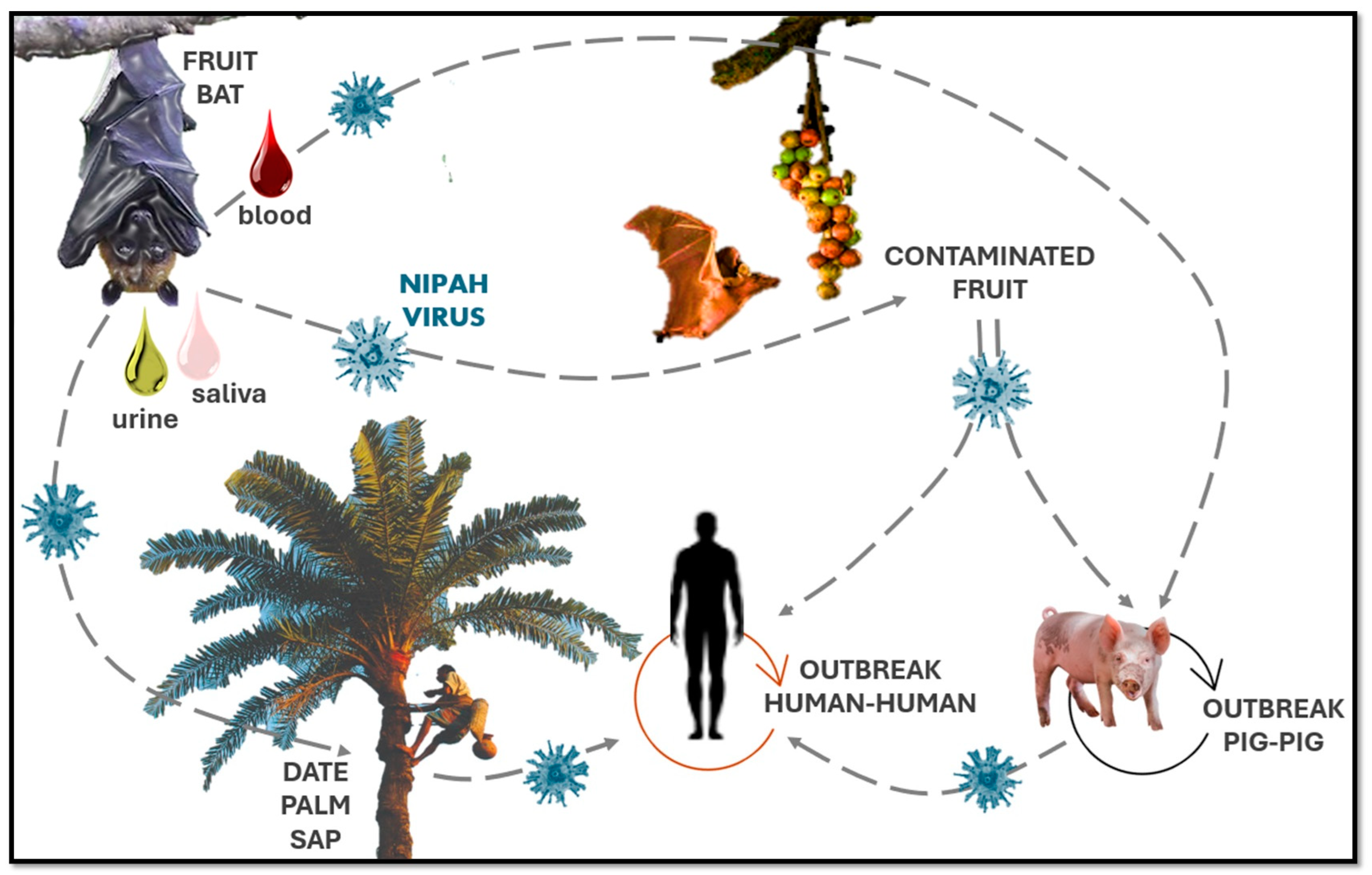
-Fruit Bats: Consuming date palm sap contaminated by fruit bats is one of the most common transmission routes.
-Infected Pigs: Direct contact with infected pigs’ bodily fluids or tissues can also lead to infection.
-Human-to-Human Transmission: Close contact with the blood, saliva, and bodily fluids of infected individuals can lead to person-to-person transmission. Healthcare workers and family members are at the highest risk.
Preventive Measures
-Avoid Wild Animals: To reduce the risk of exposure to fruit bats, it is essential to avoid consuming fruit that may have been contaminated. Pay special attention to fruit with bite marks or visible damage.
-Stay Informed: If you are traveling to India or Southeast Asia, stay updated with local health authorities’ advice and avoid regions with reported outbreaks.
-Animal Quarantine: Strengthen animal testing and quarantine measures at borders to prevent infected animals from crossing into other countries.
Clinical Features of Nipah Virus Infection
Nipah virus primarily attacks the brain, leading to encephalitis, seizures, and respiratory distress. The symptoms often mimic the flu in the early stages, making it difficult to diagnose.
-Initial Symptoms: Fever, headache, muscle pain
-Progression: Rapidly progresses to encephalitis, seizures, and respiratory distress
-Fatal Outcome: WHO warns that patients can slip into a coma within 24 to 48 hours.
-Long-Term Effects: Survivors may experience lasting neurological damage, including personality changes and epilepsy.
Testing and Detection
- Molecular PCR for Rapid Identification
In response to the ongoing outbreak, Macro & Micro-Test has developed a molecular testing solution for Nipah virus (NIV). The high-sensitivity RT-PCR kits are designed for early diagnosis at hospitals and disease control centers.
These tests offer accurate screening and emergency diagnosis. They can be used on oral and nasopharyngeal swabs, cerebrospinal fluid, serum, and urine samples with a sensitivity of 500 copies/ml.
- NGS for Epidemiological Research and Disease Control Tracing
Additionally, Macro & Micro-Test has capabilities in high-throughput sequencing for epidemiological studies and pathogen tracing. With this technology, the virus can be identified within six hours, providing critical support in outbreak management.
The Nipah virus is a formidable threat with no current cure. It requires rapid detection and stringent preventive measures to control its spread. As the situation evolves, it is essential for healthcare providers, travelers, and governments to stay vigilant and take necessary precautions to prevent further outbreaks.
For details: marketing@mmtest.com
|
Cat.No. |
Product Name |
Packaging |
| HWTS-FE091 | Nipah virus nucleic acid detection kit (Fluorescent PCR method) – 25/50 tests/box | 25/50 tests/kit |
| HWKF-TWO424B | Ultra-sensitive Environmental Virus Whole Genome Enrichment Kit (Probe Capture – for Illumina ) | 16/24 tests/kit |
| HWKF-TWO425B | Ultra-sensitive Environmental Virus Whole Genome Enrichment Kit (Probe Capture – for MGI) | 16/24 tests/kit |
| HWKF-TWO861B | Nipah Virus Whole Genome Enrichment Kit (Probe Capture – for Illumina) | 16/24 tests/kit |
| HWKF-TWO862B | Nipah Virus Whole Genome Enrichment Kit (Probe Capture – for MGI) | 16/24 tests/kit |
Post time: Jan-27-2026
