A newly emerged influenza variant—Influenza A(H3N2) Subclade K—is driving unusually high influenza activity across multiple regions, placing significant pressure on global healthcare systems. At the same time, diagnostic innovations ranging from rapid antigen screening to fully automated molecular testing to full-genome sequencing are reshaping how we detect, confirm, and understand evolving viral threats.
Together, these developments mark a shift toward a more precise, layered approach to respiratory infectious disease management.
A Variant That Changes the Game: What Makes Subclade K Different
Subclade K represents a newly evolved genetic branch within the H3N2 lineage, shaped by continuous mutations in the hemagglutinin (HA) protein. While antigenic drift is expected, Subclade K has rapidly distinguished itself through two critical properties:
Immune Escape
Key HA mutations alter the virus’s antigenic profile, reducing its match with:
-Strains included in current influenza vaccines
-Immunity built from recent infections
This results in a higher rate of breakthrough infections.
Enhanced Transmission Fitness
Structural changes may improve the virus’s ability to bind to receptors in the upper respiratory tract, giving Subclade K a competitive edge in transmission.
Global Impact
Surveillance data from Asian and European countries show Subclade K accounting for over 90% of recent H3N2 detections. Its rapid spread has contributed to earlier flu seasons and increased healthcare burden, highlighting the need for differentiated detection strategies tailored to clinical, community, and public health settings.
A Three-Tier Diagnostic Framework for Subclade K
A rapidly evolving influenza variant requires a tiered, complementary diagnostic strategy that enables:
-Rapid screening in community settings
-Fast, precise confirmation in clinical environments
-deep genomic analysis for surveillance and research
Below is the integrated three-solution framework.
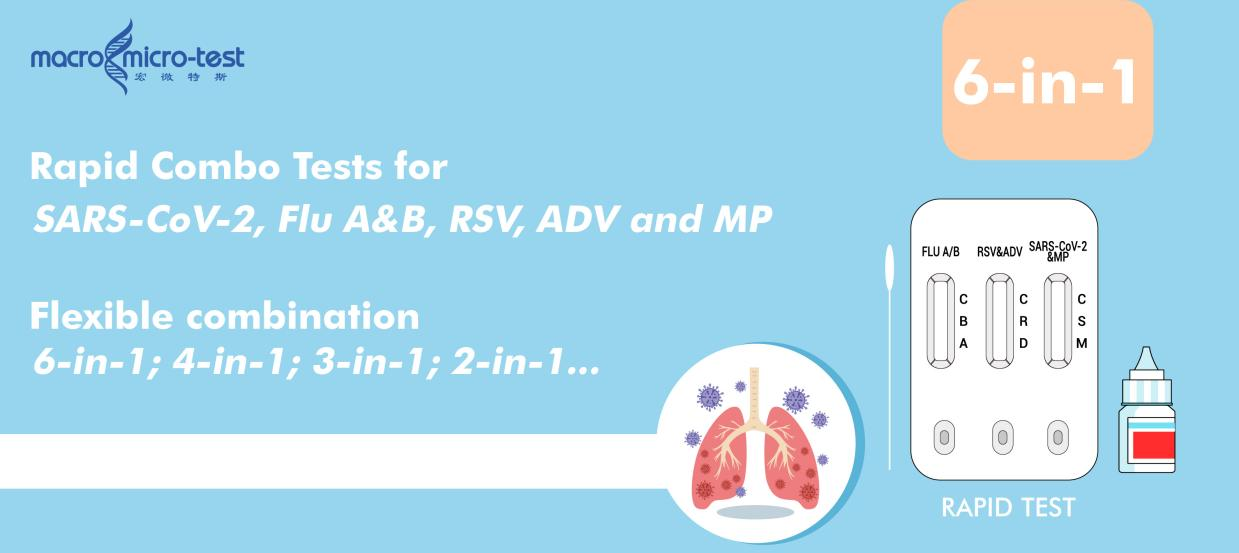
1. Rapid Screening: flexible 2~6-in-1 Antigen Test (Immunochromatography)
Ideal for:
Primary care clinics, outpatient departments, school health rooms, workplace clinics, and home self-testing.
Why it matters:
These settings require immediate triage and quick decisions to prevent spread and guide next steps.
Key Features:
-Simple, equipment-free operation
-Results available in 15 minutes
Enables rapid preliminary identification of Influenza A & B infection or other most common respiratory infections.
This test forms the first line of community-level detection, helping quickly identify suspected cases and determine whether molecular confirmation is needed.
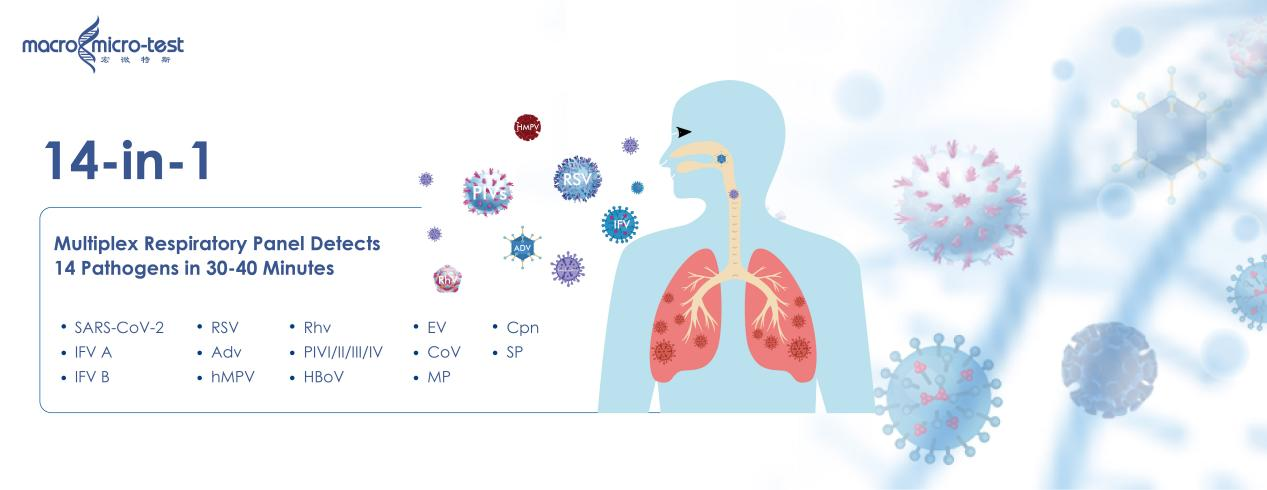
1. Rapid Molecular Confirmation: AIO800 Fully Automated Molecular Detection System+14-in-1 Respiratory Detection Kit
Ideal for:
Hospital emergency departments, inpatient wards, fever clinics, and regional diagnostic laboratories.
Why it matters:
Given Subclade K’s immune escape and overlap of symptoms with other respiratory pathogens, precise identification is essential for:
-Deciding on antiviral treatment such as oseltamivir
-Distinguishing influenza from RSV, adenovirus, or other pathogens
-Making rapid hospitalization or isolation decisions
Key Features:
-True “sample-in, result-out” fully automated workflow
-Delivers nucleic acid test results in 30–45 minutes
-Multiplex real-time PCR panels detect 14 respiratory pathogens even at very low viral load.
The AIO800 serves as the clinical core of modern influenza diagnostics, enabling fast, accurate confirmation and supporting real-time public health surveillance.
3. Deep Viral Investigation: Full-Genome Sequencing of Influenza Viruses
Ideal for:
Centers for Disease Control, research institutes, viral surveillance sites, and national or regional public health laboratories.
Why it matters:
Subclade K—and future variants—must be continuously monitored at the genomic level to understand:
-Antigenic drift
-Antiviral resistance mutations
-Emergence of new variants
-Transmission networks and outbreak origins
Key Features:
-End-to-end service from sample extraction to library preparation, sequencing, and bioinformatic analysis
-Provides complete viral genome sequences
-Enables analysis of mutation profiles, phylogenetic trees, and evolutionary dynamics
Whole-genome sequencing represents the deepest diagnostic layer, providing insights that inform vaccine updates, policy decisions, and global
surveillance frameworks.
Toward a Precision-Driven Influenza Control System
The combination of a rapidly adapting viral threat and advanced diagnostic technologies is driving a transformation in public health strategy.
1. From Symptom-Based Guesswork to Precision Layered Testing
Antigen screening → molecular confirmation → genomic tracking form a complete diagnostic pipeline.
2. From Reactive Response to Real-Time Awareness
Frequent rapid testing and continuous genomic data support early warnings and dynamic policy adjustment.
3. From Fragmented Measures to Integrated Control
Vaccination, rapid diagnostics, antiviral therapy, and public health interventions create a coordinated defense system.
Within this framework, the antigen test provides the frontline filter, the AIO800 delivers clinical precision, and full-genome sequencing offers strategic depth—together forming the strongest defense against Subclade K and future influenza variants.
Post time: Dec-10-2025